Exploit Analysis Decoding Moola Market’s Price Manipulation Attack
Multiple token drain in Moola Market, a liquidity protocol suffered a loss of $9.1 million.
TL;DR
On October 18, 2022, Moola Market was exploited for $9.1 million. The exploit involves draining multiple tokens, including 8.8 million $CELO tokens valued at $6.6 million, 765k $cEUR tokens worth $0.7 million, 1.8 million $MOO tokens worth $1.2 million, and 644k $cUSD tokens worth $0.6 million.
Introduction to Moola Market
Moola Market is a non-custodial liquidity protocol on Celo ecosystem that is democratizing access to yield and credit.
Vulnerability Assessment
The attacker manipulated the price of the low-liquidity native $MOO token by acquiring a portion of it, and then used them as a collateral to borrow $CELO tokens back-and-forth to take away the funds. The exploit did not require the creation of a newer smart contract.
Steps
Step 1:
The exploiter initially funded 0x0c686ac4ecb6be587c045ddd07379b094ee6f0f01085743a3ebe62f60465c5ff his account with $CELO tokens.
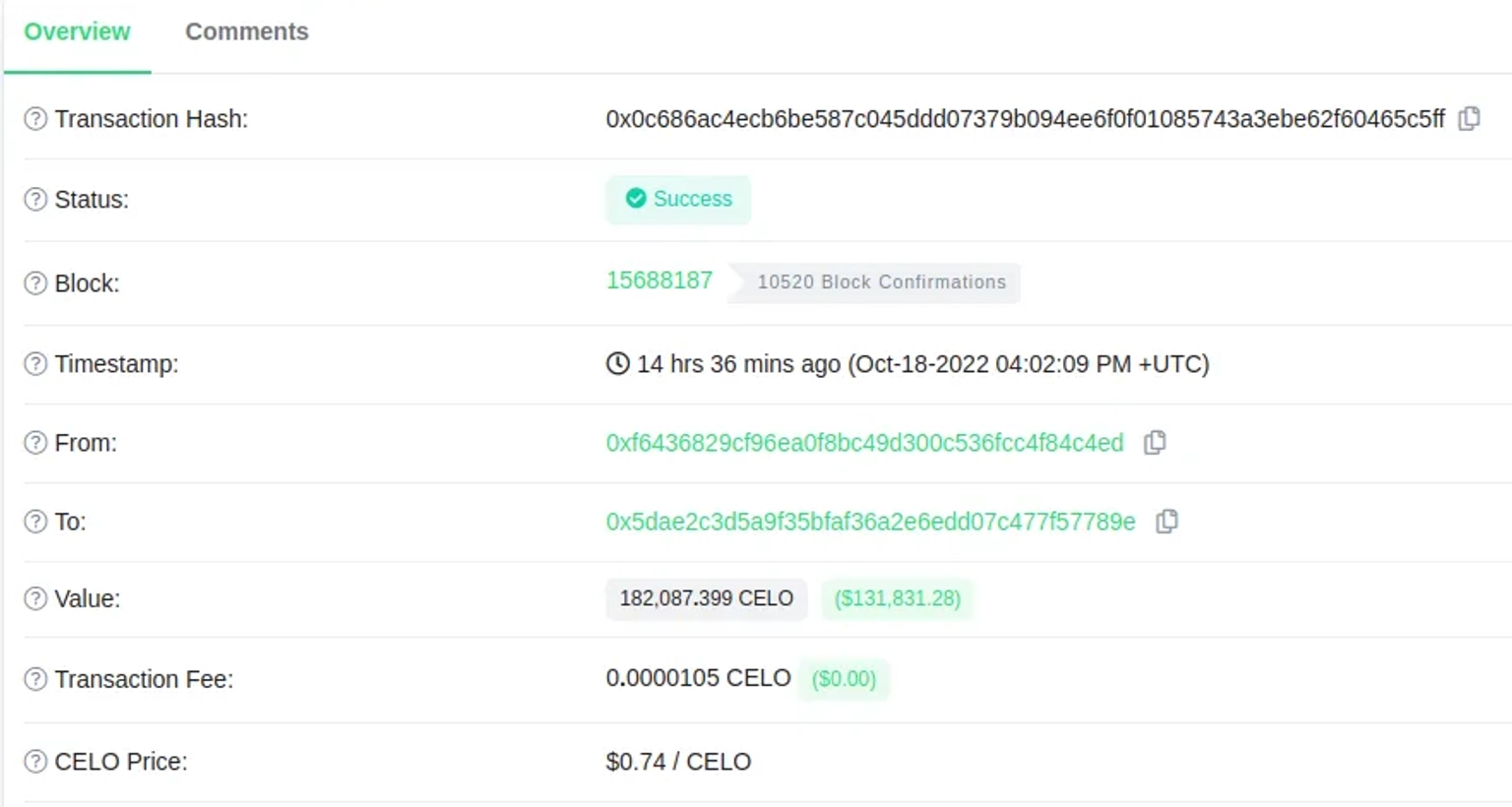
Step 2:
They lent 60k $CELO tokens to Moola and then borrowed 1.8 million $MOO tokens to use them as collateral.
Step 3:
According to the logic of collateralized lending, individuals who lock $MOO tokens can borrow out an equivalent amount of $CELO tokens.
Step 4:
After that, using the remaining $CELO tokens, they started to pump the $MOO token price, and use it as a collateral to borrow all other tokens.
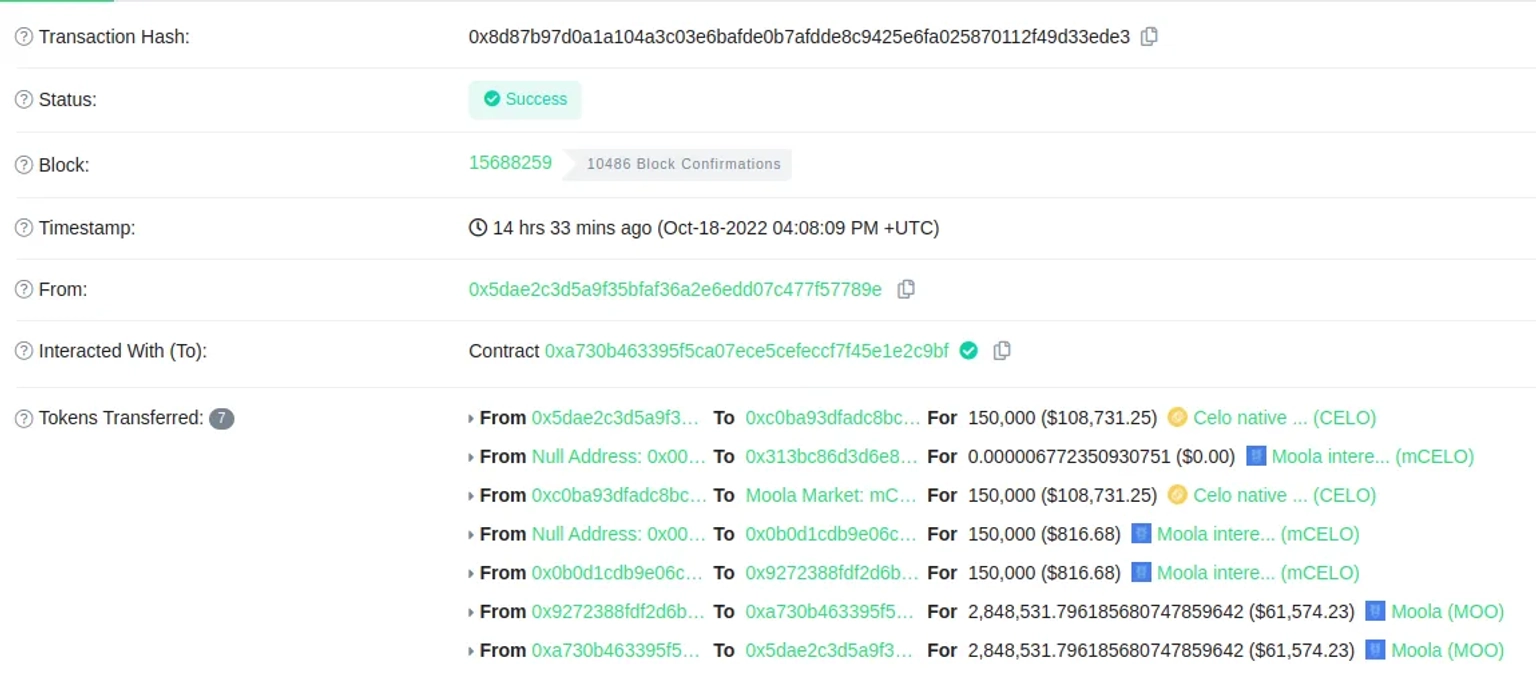
Step 5:
The attacker kept doing this until the price of the $MOO token had increased by 6,400%.
Step 6:
At the end of this cycle, they transferred all the tokens to this address 0x95b5579b323ddc6cd290bd4da6e56ba019588efc.
Aftermath
After the announcement of the incident, the team halted all the activity on Moola. The team tweeted that they had informed law enforcement agencies and taken steps to make liquidating the assets difficult.
A bounty payment was also announced in exchange for returning the funds within the next 24 hours of the incident, after which 93.1% of stolen funds were returned to the Moola governance multi-sig. The attacker appears to have kept the remaining funds, earning around $500,000 as a bug bounty.
How to Prevent Such an Attack Vector
Price manipulation results from logical flaws in DeFi applications; therefore, it is necessary to examine multiple smart contracts and comprehend the high-level semantics of DeFi applications in order to detect it.
A team can also mitigate all of these risks to a greater extent by utilizing oracles such as ChainLink.